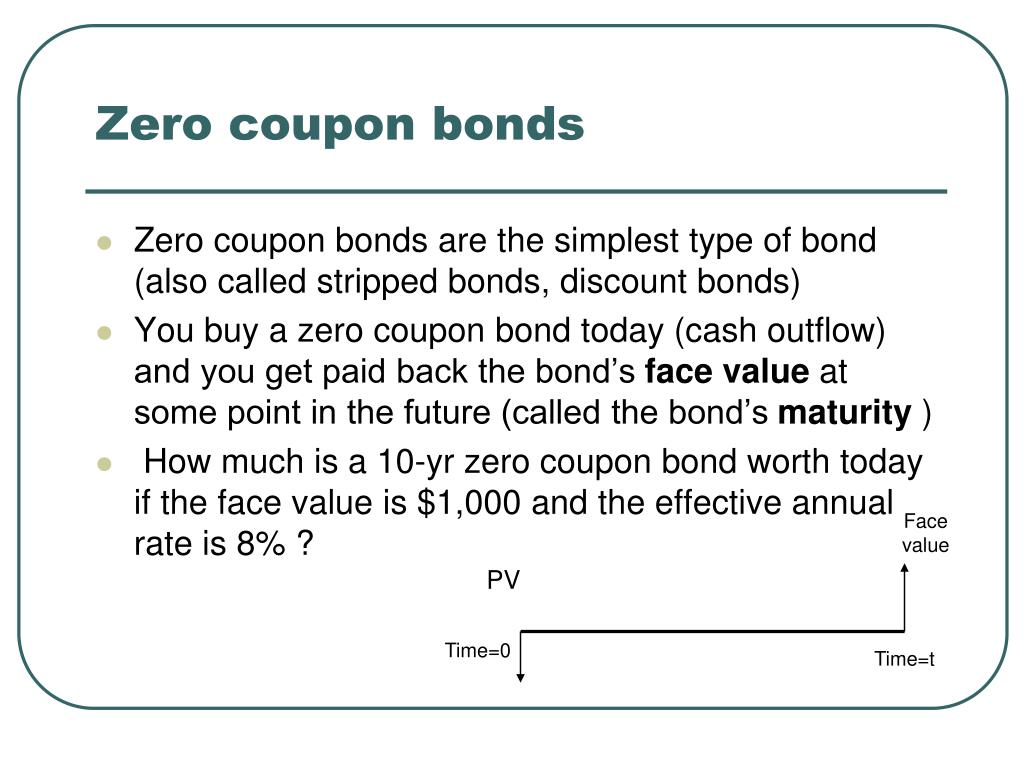
41 valuing zero coupon bonds
Zero - Coupon Bonds - Economy Blatt Zero - coupon bonds are also called pure discount bonds as they trade at a discount, a price lower than the face value prior to its maturity date. Suppose you have purchased a one - year, risk - free, zero coupon bond which has an initial price of $ 144,927. The face value of the bond is $150,000. Swaps in Finance | Definition | Examples | Valuation Types of Swaps in Finance. There are several types of Swaps transacted in the financial world. They are a commodity, currency, volatility, debt, credit default, puttable, swaptions, Interest rate swap, equity swap Equity Swap Equity Swaps is defined as a derivative contract between two parties that involve the exchange of future cash flows. There are two basis of determining cash …
Zero Coupon Bond Calculator - What is the Market Value? What's the zero coupon bond pricing formula? The zero coupon bond price formula is: \frac {P} { (1+r)^t} (1+ r)tP. where: P: The par or face value of the zero coupon bond. r: The interest rate of the bond. t: The time to maturity of the bond.

Valuing zero coupon bonds
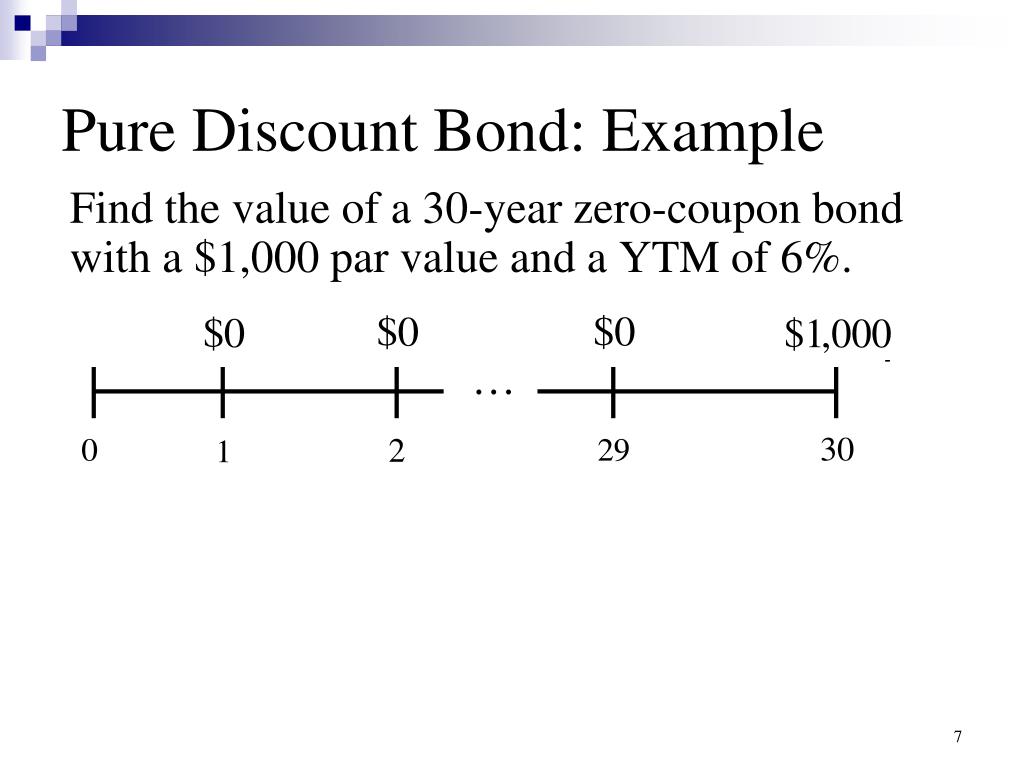
Valuing a zero-coupon bond | Mastering Python for Finance - Packt Zero-coupon bonds are also called pure discount bonds. A zero-coupon bond can be valued as follows: Here, is the annually compounded yield or rate of the bond, and is the time remaining to the maturity of the bond. Let's take a look at an example of a 5-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $100. The yield is 5 percent, compounded annually. Solved 2. Valuing a Zero-Coupon Bond. Assume the following - Chegg Answer to Solved 2. Valuing a Zero-Coupon Bond. Assume the following Chapter 7 -- Stocks and Stock Valuation - California State … Example: a firm can issue a 10-year 8% coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 to raise money. The firm pays interest semiannually. The net price for each bond is $950. What is the cost of debt before tax? If the firm’s marginal tax rate is 40%, what is the cost of debt after tax? Cost of debt before tax = rd = 8.76%
Valuing zero coupon bonds. All the 21 Types of Bonds | General Features and Valuation | eFM Jun 13, 2022 · Zero-Coupon Bonds. A zero-coupon bond is a type of bond with no coupon payments. It is not that there is no yield; the zero-coupon bonds are issued at a price lower than the face value (say 950$) and then pay the face value on maturity ($1000). ... For valuing the above bond using the present value technique, it is of utmost importance to find ... Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia General Advantages of Zero-Coupon Bonds Why would anyone want a bond without the interest? Well, for one thing, zero-coupon bonds are bought for a fraction of face value. For example, a $20,000... What does it mean if a bond has a zero coupon rate? - Investopedia Zero Coupon Bonds A zero coupon bond generally has a reduced market price relative to its par value because the purchaser must maintain ownership of the bond until maturity to turn a profit. A bond... Chapter 12: The Cost of Capital - California State University, … Title: Chapter 12: The Cost of Capital Subject: Gallagher and Andrew Author: Gallagher Last modified by: kuhlejl Created Date: 6/19/1997 4:16:34 PM
How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price - Double Entry Bookkeeping The zero coupon bond price is calculated as follows: n = 3 i = 7% FV = Face value of the bond = 1,000 Zero coupon bond price = FV / (1 + i) n Zero coupon bond price = 1,000 / (1 + 7%) 3 Zero coupon bond price = 816.30 (rounded to 816) Valuing a zero-coupon bond | Mastering Python for Finance - Packt Zero-coupon bonds are also called pure discount bonds. A zero-coupon bond can be valued as follows: Here, y is the annually-compounded yield or rate of the bond, and t is the time remaining to the maturity of the bond. Let's take a look at an example of a five-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $ 100. The yield is 5%, compounded annually. Zero-Coupon Bond Value | Formula, Example, Analysis, Calculator The zero-coupon bond value refers to the current value of a zero-coupon bond. This formula requires three variables: face value, interest rate and the number of years to maturity. The zero-coupon bond value is usually expressed as a monetary amount. This equation is sensitive to interest rate fluctuations. Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia If the debtor accepts this offer, the bond will be sold to the investor at $20,991 / $25,000 = 84% of the face value. Upon maturity, the investor gains $25,000 - $20,991 = $4,009, which translates...
Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Calculator [Excel Template] To calculate the price of a zero-coupon bond - i.e. the present value (PV) - the first step is to find the bond's future value (FV), which is most often $1,000. The next step is to add the yield-to-maturity (YTM) to one and then raise it to the power of the number of compounding periods. What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? - The Motley Fool Zero-coupon bonds compensate for not paying any interest over the life of the bond by being available for far less than face value. Put another way, without a deep discount, zero-coupon bonds ... Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula John is looking to purchase a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 and 5 years to maturity. The interest rate on the bond is 5% compounded annually. What price will John pay for the bond today? Price of bond = $1,000 / (1+0.05) 5 = $783.53 The price that John will pay for the bond today is $783.53. Example 2: Semi-annual Compounding Zero-Coupon Bonds - Acing Finance Valuing Zero-Coupon Bonds. To find the present value of a zero-coupon bond, we take the face value and divide it by the interest rate to the power of time to maturity. The formula is. Where r is the interest rate, and t is the time to maturity. Example: A 3-year zero-coupon bond is issued with a face value of $1000 and an interest rate of 8%.
Pricing of Swaps, Futures, & Forward Contracts | CFA Institute With a basic understanding of pricing and valuing a simple interest rate swap, it is a straightforward extension to pricing and valuing currency swaps and equity swaps. The solution for each of the three variables, one notional amount (NA a ) and two fixed rates (one for each currency, a and b), needed to price a fixed-for-fixed currency swap are :
Zero Coupon Bonds Explained (With Examples) - Fervent Valuing Zero Coupon Bonds on Excel® We'll be using Excel's "PRICE" function to value Swindon Plc's bond. The first thing you want to do is setup your spreadsheet with a pro-forma / template that consists of the all different variables you'll need. The "PRICE" function on Excel® requires:
Zero Coupon Bond Value - Formula (with Calculator) - finance formulas A 5 year zero coupon bond is issued with a face value of $100 and a rate of 6%. Looking at the formula, $100 would be F, 6% would be r, and t would be 5 years. After solving the equation, the original price or value would be $74.73. After 5 years, the bond could then be redeemed for the $100 face value.
Valuing a zero-coupon bond | Mastering Python for Finance - Second Edition A zero-coupon bond is a bond that does not pay any periodic interest except on maturity, where the principal or face value is repaid. Zero-coupon bonds are also
Fundamentals of Finance | Coursera Holding Period Return and Yield to Maturity for Zero-Coupon Bonds 10m. Calculating the Holding Period Return on a Coupon Bond 10m. Topic 3 Lecture Slides 10m. Topic 3 Lecture Notes 10m. 1 practice exercise. Module 2 Quiz 30m. Week. 3. ... From valuing claims and making financing decisions, to elements of a basic financial model, the coursework ...
Zero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to Maturity ... Let's say a zero coupon bond is issued for $500 and will pay $1,000 at maturity in 30 years. Divide the $1,000 by $500 gives us 2. Raise 2 to the 1/30th power and you get 1.02329. Subtract 1, and you have 0.02329, which is 2.3239%. Advantages of Zero-coupon Bonds Most bonds typically pay out a coupon every six months.
ACCT 223 | Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet 2. Characteristics of Bonds a. A bond's _____ is generally $1,000 and represents the amount borrowed from the bond's first purchaser. b. A bond issuer is said to be in _____ if it does not pay the interest or the principal in accordance with the terms of the indenture agreement or if it violates one or more of the issue's restrictive covenants.
What are bond spreads? - Financial Pipeline Feb 19, 2016 · The yield spread or “curve spread ” between these two bonds is 1.6%, which reflects the interest rate between the two bonds and the conditions of monetary policy. Coupon Spreads are spreads that reflect the differences between bonds with different interest rate coupons. For example, the Government of Canada has issued two bonds that are due ...
SOPHIA PATHWAYS Principles of Finance unit 2 - Quizlet b.)Longer-term bonds are less sensitive to interest rate risk than shorter-term bonds. c.)Bonds held until maturity have greater exposure to interest rate risk. d.)It stems from the fact that coupon rates and market interest rates are directly correlated.
Reserve Bank of India - Frequently Asked Questions STRIPS in G-Secs ensure availability of sovereign zero coupon bonds, which facilitate the development of a market determined zero coupon yield curve (ZCYC). ... FIMMDA gives out the information on corporate bond spreads for various ratings of bonds. While valuing a bond, the appropriate spread has to be added to the corresponding CG yield and ...
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don't mature for ten, fifteen, or more years.
How to Calculate Yield to Maturity of a Zero-Coupon Bond - Investopedia With no coupon payments on zero-coupon bonds, their value is entirely based on the current price compared to face value. As such, when interest rates are falling, prices are positioned to rise ...
Chapter 7 -- Stocks and Stock Valuation - California State … Example: a firm can issue a 10-year 8% coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 to raise money. The firm pays interest semiannually. The net price for each bond is $950. What is the cost of debt before tax? If the firm’s marginal tax rate is 40%, what is the cost of debt after tax? Cost of debt before tax = rd = 8.76%
Solved 2. Valuing a Zero-Coupon Bond. Assume the following - Chegg Answer to Solved 2. Valuing a Zero-Coupon Bond. Assume the following
Valuing a zero-coupon bond | Mastering Python for Finance - Packt Zero-coupon bonds are also called pure discount bonds. A zero-coupon bond can be valued as follows: Here, is the annually compounded yield or rate of the bond, and is the time remaining to the maturity of the bond. Let's take a look at an example of a 5-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $100. The yield is 5 percent, compounded annually.









Post a Comment for "41 valuing zero coupon bonds"